Educating Pet Owners on Medical Causes of Aggression in Cats
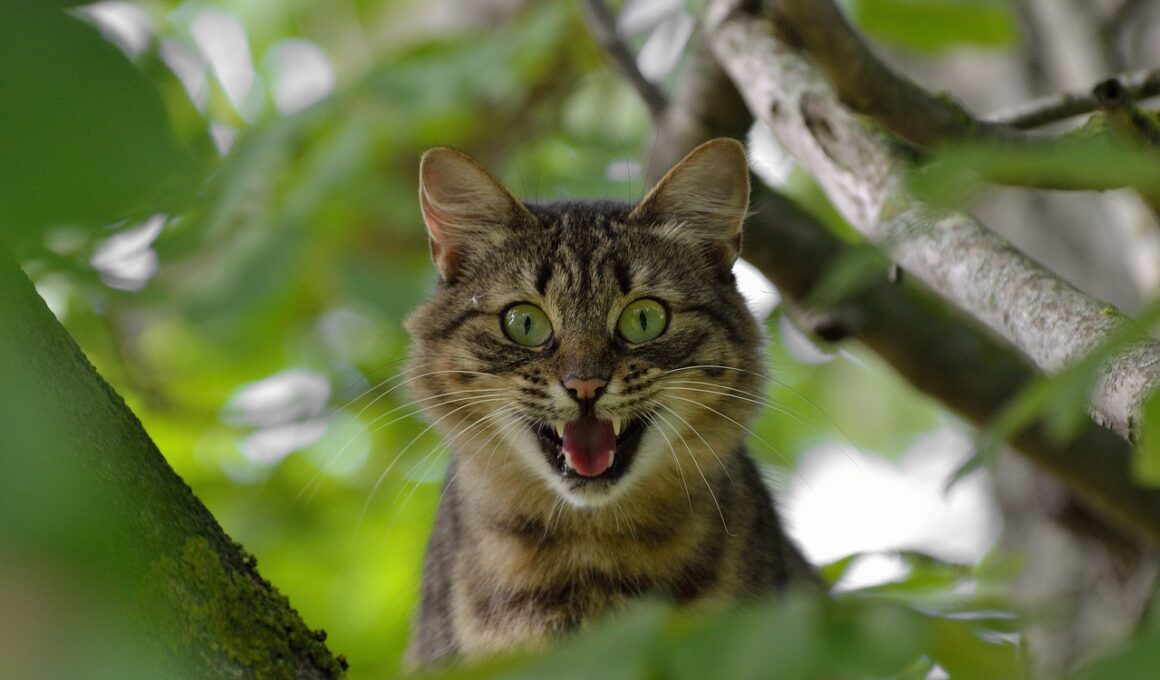
Aggression in cats can stem from various medical conditions, often leading to misunderstandings. Pet owners must recognize signs indicating that their pet’s behavior may not be purely behavioral. Pain or illness can provoke aggression, making awareness crucial for pet owners. It is essential to observe changes in your cat’s behavior, as these may signal underlying health issues. Typical conditions that could lead to aggression include hyperthyroidism, arthritis, or dental disease. Understanding these medical factors is vital for managing your cat’s conduct effectively. Knowing when to consult a veterinarian is informative, as prompt care can alleviate pain and reduce aggressive tendencies. Owners must also avoid assuming that aggression is solely related to temperament; physical pain often leads to defensive behaviors. To better understand your feline, regular check-ups should be scheduled with veterinary professionals. Moreover, consider providing a calming environment when aggression is noticed, as stress can exacerbate aggression related to medical conditions. Recognizing these connections can lead to better outcomes for both the cat and the owner, fostering a peaceful home atmosphere.
To effectively mitigate aggression, understanding how conditions impact your cat’s behavior is essential. A common cause lies in pain-induced aggression, where cats react defensively when they feel threatened. Consider mitigating potential stressors in their environment, such as loud noises or unwanted visitors. This adjustment could decrease territorial aggression, which often stems from anxiety or a sense of vulnerability. Another critical aspect includes recognizing that aggression may also arise from neurological conditions, leading to erratic behaviors. For these situations, medical interventions may include medication or specific behavioral therapies. Pet owners should take aggression seriously; it can become habitual unless addressed properly. Observing your cat’s nuanced signals can aid in prevention; be attentive to body language and vocalizations that indicate distress. Moreover, ensure your cat receives ongoing medical evaluations, especially as they age. Factors such as hormonal imbalances can emerge over time and lead to aggression. Encouraging a regular schedule for check-ups creates the opportunity to identify issues early. Addressing medical causes profoundly impacts behavior management strategies, ultimately enhancing the bond between pet and owner.
Identifying Signs of Medical Issues in Felines
Identifying potential medical causes behind aggressive behavior is key to cat ownership. Changes in appetite, litter box habits, and grooming patterns may indicate a problem. Moreover, irritability or increased vocalization should not be overlooked, as these may signal underlying issues. A comprehensive understanding of various feline health conditions can lead to quicker diagnoses. For instance, cats suffering from arthritis may exhibit aggression when touched in painful areas. Moreover, hyperthyroidism can cause hyperactivity, leading to overstimulation and aggression. Veterinary consultations are necessary to rule out these concerns, and owners should prepare for visits by documenting behavioral changes. In conjunction with medical insights, veterinarians may conduct physical examinations and blood tests to accurately identify issues. Understanding when to seek veterinary help can save a pet from ongoing suffering, therefore, do not hesitate if you notice unusual aggression. Furthermore, educating oneself about common stressors and health markers in cats enhances one’s ability to provide proper care. By improving awareness, pet owners can foster a healthier and more harmonious environment that ultimately promotes better behavioral health.
In instances where medical conditions have been diagnosed, creating a supportive home environment is essential. This practice involves minimizing stressors that can aggravate aggressive behavior. Simple adjustments, such as creating separate spaces for each cat in multi-pet households, can help. These spaces allow pets to retreat whenever they feel threatened or overstimulated. Additionally, investing in calming products like pheromone diffusers or calming collars can aid in emotional stability. It is also beneficial to engage in gentle play routines that accommodate your cat’s physical limitations. Tailoring activities based on their capabilities leads to more successful interactions. Engaging in low-stress behaviors demonstrates an understanding of their needs and builds trust. Enrichment activities, such as puzzle feeders or hiding treats, can also keep a cat’s mind active and engaged while reducing frustration. Avoid punishing aggressive behavior; instead, focus on redirecting negative energy towards appropriate outlets. Lastly, provide regular mental and physical stimulation, essential for maintaining overall well-being. Consistency and care in approach can significantly enhance any situation, improving both behavior and emotional health.
The Importance of Regular Vet Check-ups
Regular veterinary check-ups play a significant role in preemptively addressing aggression in cats. These appointments become increasingly important as cats age since older felines are particularly susceptible to various health conditions leading to aggression. For example, chronic pain can develop without direct evidence, thereby influencing behavior. Regular blood tests help detect hidden health issues such as hyperthyroidism, which can cause increased irritability and aggression. Moreover, a routine examination allows for comprehensive assessments of dental health, which, if neglected, can lead to severe discomfort and aggressive outbursts. It is crucial for owners to establish a relationship with a veterinarian who understands feline behavior and medical care. Veterinarians can also provide tailored advice regarding diet, supplements, and lifestyle changes that promote overall health. Understanding how these factors contribute to behavior helps owners make informed decisions regarding appropriate interventions. Pet owners should keep track of any noticeable behavioral changes for discussion during vet visits. Record-keeping allows veterinary professionals to discern patterns that may not be immediately apparent. Keeping all these aspects in check leads to healthier, happier, and more well-adjusted feline companions.
Medication may be required for certain medical conditions impacting aggression in cats. Should a vet determine a medical issue responsible, prescribed treatments aim to alleviate pain or modify behavior. Anti-inflammatory medication can help with pain relief in arthritic cats, leading to improved mood. In severe cases, veterinarians might recommend anti-anxiety medications or mood stabilizers. Understanding the nuances of your cat’s condition helps determine the right approach. Additionally, pet owners should remain informed about possible side effects associated with prescribed medications. Monitoring any changes necessitates vigilance and communication with the veterinarian for optimal adjustments. Furthermore, ensuring correct dosages is crucial to preventing adverse reactions. During treatment, maintaining a loving demeanor and providing adequate support fosters a healthier environment. Reinforcing positive behaviors through reward-based training can also help, as it generates trust. Building a strong bond during this process can mitigate fear and confusion associated with medication. It is vital to combine medical treatment with behavioral observation for achieving lasting behavioral improvements. Addressing both mental and physical health enhances overall well-being, fostering a balanced existence for every feline companion.
Conclusion: The Path to Understanding and Support
Conclusively, understanding medical causes of aggression toward cats enhances pet ownership quality. Highly complex interactions between health conditions and behavior require comprehensive evaluations. Pet owners who are proactive about their cat’s health improve not only the quality of life for their feline but also establish healthier relationships. Acknowledging that aggression may indeed be symptomatic of a medical problem assists in preventing misinterpretations of a cat’s nature. Equally important is fostering open lines of communication with veterinary professionals. Their insights can guide responsible pet ownership, ensuring informed decisions. Furthermore, owners should continuously educate themselves about feline health to empower their decision-making abilities. Supporting mental health through enrichment activities reduces aggression and improves life quality. Ultimately, a strong commitment to understanding each pet’s unique needs will lead to better behavioral outcomes. Together, with medical assistance and owner support, managing aggression in cats becomes an achievable goal. Crafting a safe and nurturing environment is essential for all pets, enabling each to thrive. Recognizing aggression as a complex issue helps streamline interventions, leading to improved relationships.
This is another paragraph with exactly 190 words…