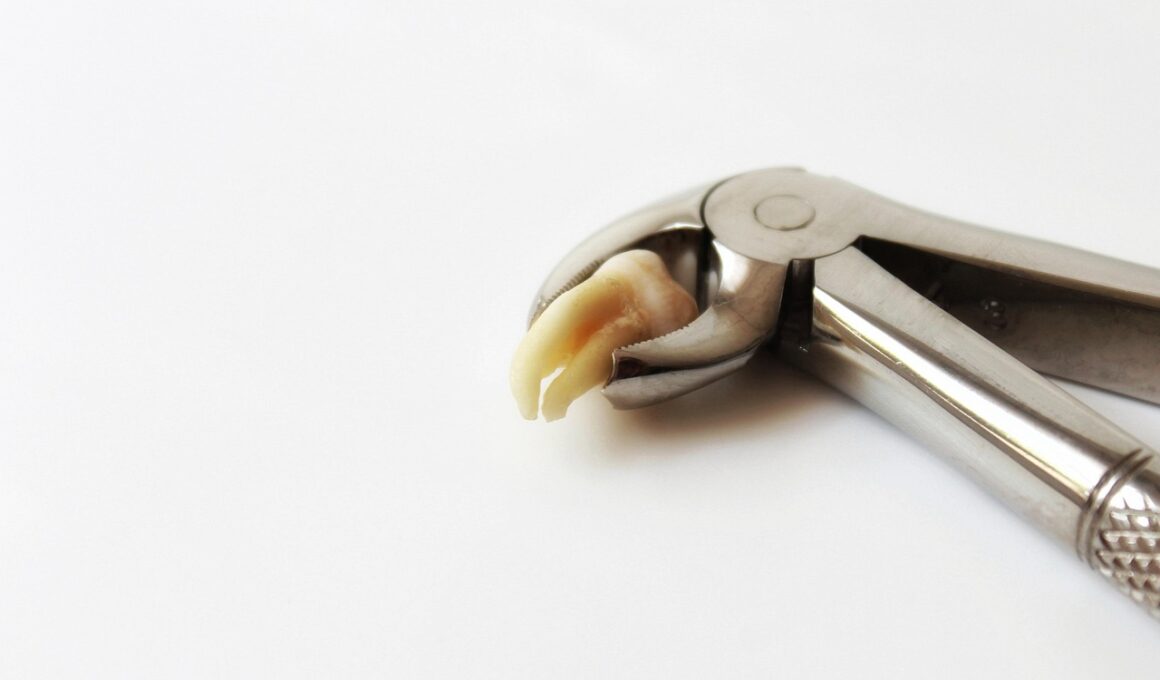
Common Reasons for Cat Tooth Extractions
Cat tooth extractions are common veterinary procedures, often required for various dental issues. One significant reason for performing an extraction is periodontal disease. This condition occurs when plaque builds up on the teeth, leading to inflammation and infection of the gums. If left untreated, it can cause severe pain and eventual tooth loss. Another common cause is tooth resorption, which affects many cats and is characterized by the deterioration of the tooth structure. This painful condition leads to teeth being damaged or breaking down, necessitating their removal. Additionally, dental fractures can occur due to injury or chewing on hard objects, leading to discomfort and potential infection. In some cases, extractions may be required for retained baby teeth that do not fall out as expected. These retained teeth can create issues with the alignment of adult teeth. Moreover, tumors or other growths in the mouth may sometimes require tooth extraction to eliminate them. Overall, timely veterinary intervention is crucial for maintaining a cat’s dental health and quality of life, preventing further complications that can arise from untreated dental issues.
Another reason for cat tooth extractions is dental abscesses, which are pockets of pus that form around the tooth roots due to infection. These abscesses can be extremely painful and are often associated with periodontal disease or a fractured tooth. The accumulation of bacteria leads to swelling and discomfort, making extraction necessary to relieve pain and promote healing. Additionally, certain breeds of cats may be predisposed to dental problems, necessitating more frequent dental evaluations. Regular dental check-ups can help identify issues before they become severe. Furthermore, systemic health issues in a cat can affect their dental health, emphasizing the importance of addressing overall wellness. Chronic kidney disease, for instance, can lead to oral problems, making dental care critical in affected cats. Preventive measures, such as proper dental hygiene, appropriate chew toys, and a balanced diet, are essential in reducing the risk of dental disease. Ultimately, understanding the various reasons behind tooth extractions can help cat owners take proactive steps in managing their feline’s dental care. Early intervention ensures a better quality of life and helps prevent pain associated with dental diseases.
Periodontal Disease in Cats
Periodontal disease is prevalent among cats and is primarily caused by a buildup of plaque and tartar. This accumulation leads to inflammation of the gums, known as gingivitis, which, if untreated, can progress to periodontitis. In this advanced stage, supporting tissue and bone around the teeth can be damaged. If dental health is neglected, the effects can manifest as pain, loss of appetite, and even systemic health issues because bacteria from the mouth can enter the bloodstream. Cat owners should observe their pets’ dental health regularly. Signs such as bad breath, difficulty eating, and pawing at the mouth indicate potential dental issues. Early veterinary intervention can prevent the advancement of gum disease and possible tooth loss. Maintaining a routine dental care program, including brushing your cat’s teeth and providing dental treats, can help reduce plaque formation. Regular veterinary cleanings are also recommended. In essence, being proactive about your cat’s dental care can prevent painful complications, ensuring they lead a healthy, happy life. Consulting with your veterinarian about suitable dental products and practices can significantly impact your cat’s oral health.
Another common issue that leads to tooth extractions in cats is tooth resorption. This condition is perplexing since the cause is still not entirely understood, though it seems to be linked with dental issues and possibly hormonal changes. Resorption leads to progressive damage or destruction of the tooth structure, often causing pain and discomfort for the affected cat. This often results in the necessity for veterinary intervention. Unfortunately, tooth resorption can be chronic and may affect multiple teeth simultaneously, complicating dental care and management. Signs of this condition may include reluctance to eat, pawing at the mouth, and unusual behavior while chewing. Cat owners need to recognize these signs and consult their veterinarian promptly. Early detection and intervention can relieve pain and help preserve remaining teeth when possible. Moreover, understanding the symptoms of tooth resorption can lead to better preventive care. Dental radiographs are often the best method for diagnosing this condition, as external physical examination may not reveal the extent of the problem. Veterinary dentists can then recommend the best treatment plan, which may include extraction if the resorption is severe.
Dental Fractures and Injuries
Dental fractures in cats can occur for various reasons. Cats are playful creatures and often engage in activities that may lead to injury, such as biting toys, climbing, or wrestling with other pets. Fractured teeth can be painful and may expose the tooth’s nerve, leading to infections if not treated promptly. Symptoms of a dental fracture can include signs of discomfort, eating difficulties, or swelling in the mouth area. If a cat exhibits these symptoms, a prompt veterinary visit is necessary for diagnosis and treatment. Depending on the severity of the fracture, the treatment may vary from dental bonding to full extraction of the affected tooth. In some instances, multiple fractures may necessitate the removal of several teeth at once. In addition to immediate injury, persistent dental issues can lead to fractures over time, making regular dental check-ups essential. Preventative care, including proper diet and dental hygiene practices, can also help minimize the risk of tooth fractures. Addressing any dental injuries on time will enhance a cat’s wellbeing and prevent long-term complications associated with untreated dental issues.
Retained deciduous teeth, commonly referred to as baby teeth, can also lead to necessary cat tooth extractions. While most kittens lose their baby teeth as they grow, some cats may retain these teeth, causing alignment and dental issues as adult teeth develop. Retained baby teeth can interfere with the normal eruption of the adult teeth, leading to misalignments and overcrowding. This situation can result in various dental problems, including gum disease and tooth decay. If a cat is experiencing discomfort or dental issues related to retained teeth, it’s vital to seek veterinary advice. Regular dental check-ups can help identify retained teeth early, preventing further complications. Extraction of retained primary teeth is typically straightforward and usually done under anesthesia. Post-extraction care involves monitoring the cat for any signs of discomfort or infection. Additionally, ensuring that the adult teeth come in properly is essential for long-term dental health. By collaborating with a veterinarian, a cat owner can take the necessary steps to ensure their feline friends maintain healthy teeth and gums throughout their lives. Taking early proactive measures can improve overall dental health and wellbeing.
Tumors and Growths in Cats’ Mouths
Tumors or other growths in a cat’s mouth can significantly impact dental health, necessitating tooth extractions in some cases. These growths may be benign or malignant, and they can become painful and interfere with normal eating and grooming behaviors. Regular dental check-ups allow veterinarians to monitor any unusual growths, helping to determine if they require further investigation or intervention. Identifying and diagnosing growths promptly is essential for ensuring comprehensive care and minimizing potential complications. Symptoms may include difficulty eating, excessive drooling, bad breath, or noticeable masses in the mouth. If a tumor is present, a vet may recommend biopsy and imaging to assess the tumor’s nature and extent. Depending on the diagnosis, the extraction of affected teeth may be necessary to alleviate pain or prevent the spread of malignancy. Ensuring timely veterinary consultations can significantly enhance early detection and treatment. By addressing dental tumors early and effectively, cat owners can influence their furry friends’ quality of life. Observing for changes in behavior or dental health can lead to prompt action and better long-term outcomes for cats facing these serious dental issues.
In conclusion, cat tooth extractions are common procedures that can arise from various conditions affecting oral health. Understanding the different reasons behind these extrications helps cat owners be more vigilant about their pets’ dental needs. Whether it be periodontal disease, tooth resorption, fractures, retained teeth, or oral tumors, recognizing the signs early can lead to appropriate treatment. Regular veterinary check-ups are crucial for maintaining feline dental health, enabling timely interventions that prevent severe complications. Additionally, establishing a routine for dental care at home can significantly benefit a cat’s oral hygiene. Providing dental-friendly food, toys, and preventive dental care can reduce the likelihood of developing painful conditions over time. Ultimately, prioritizing your cat’s dental health is essential for overall wellness and quality of life. Cats rely on their owners for complete care, and proactive measures ensure they remain healthy and happy. By staying informed and attentive to their dental needs, owners can help their cats avoid the discomfort associated with dental disease. Education about feline dental health will empower cat owners to be proactive and engaged in sustaining their furry friends’ well-being.