Diagnosing Ear Infections in Dogs: What to Expect
Ear infections in dogs can be distressing for both pets and their owners. Diagnosing these infections early is crucial to prevent complications and provide effective treatment. Several factors can contribute to ear infections, including allergies, excess moisture, or foreign bodies in the ear canal. Pet owners should look for specific symptoms that indicate a possible ear infection, such as excessive scratching, head shaking, redness, or swelling in the ear area. These signs may signal irritation or infection requiring veterinary assessment. Once you notice unusual behaviors or symptoms in your dog, it is advisable to consult a veterinarian for a thorough evaluation. They will perform physical examinations to visually inspect the ears and possibly collect samples for laboratory analysis. Understanding the underlying cause of the infection is vital for effective treatment planning. In many cases, addressing the root cause can significantly enhance recovery and overall ear health in canines. Always seek professional advice without delay to ensure your dog’s well-being, as prompt diagnosis can lead to a quicker recovery and better outcomes for your furry friend. A timely intervention often leads to a more comfortable and healthier dog.
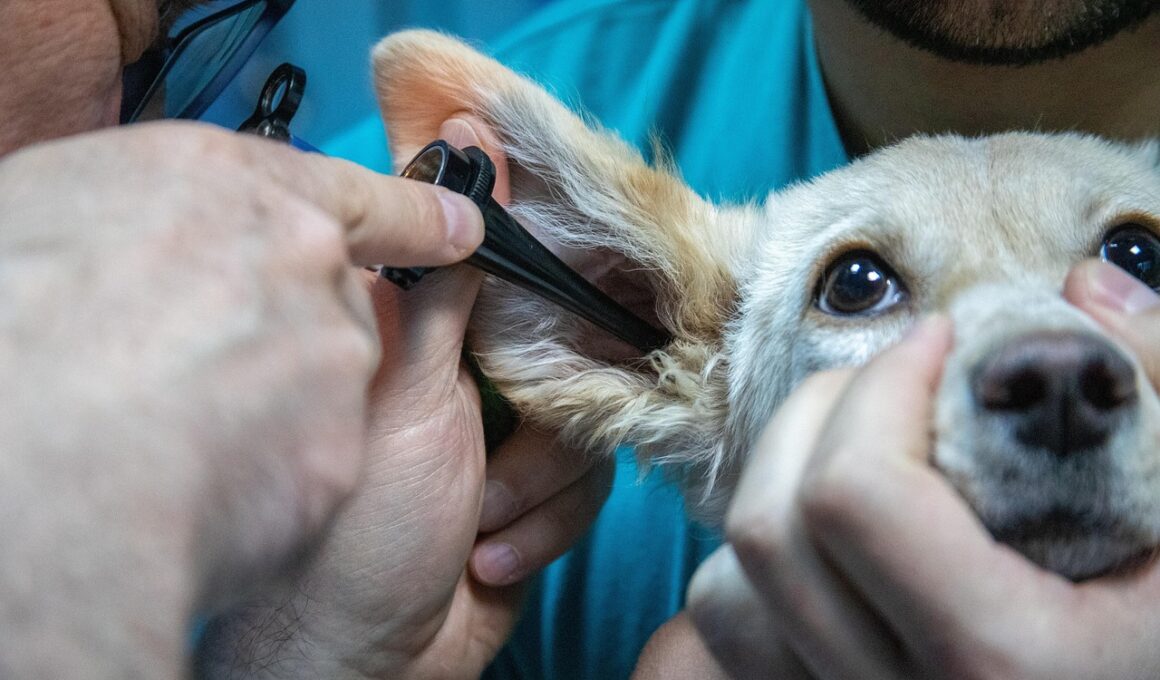
The veterinarian may perform an otoscopic examination to determine the extent of the ear infection. This involves using an otoscope, a specialized tool, to visualize the ear canal and eardrum. Understanding the anatomy of the dog’s ear can assist in diagnosing issues accurately. The ear canal of a dog is L-shaped, which means infections can be challenging to detect without the proper equipment. During this examination, the veterinarian may take samples of discharge, wax, or skin cells to identify the causative agents behind the infection. Common culprits include bacteria, yeast, mites, or even allergies. Once lab results are available, the veterinarian can customize a treatment regimen specific to the identified pathogens. In cases where allergies are present, additional testing may be required to pinpoint allergens. This information allows for better management of your dog’s health. It’s essential to follow the treatment plan precisely, including medication or topical treatments prescribed. Regular follow-ups are important to confirm that the infection has resolved. Owners should maintain vigilance to ensure similar issues do not recur in the future, establishing a proactive approach towards their dog’s ear health.
Identifying Common Symptoms
Recognizing the symptoms of ear infections in dogs is key to timely diagnosis and treatment. Dogs may exhibit various signs, such as persistent shaking of the head, scratching at the ears, or rubbing against furniture. These actions indicate discomfort or irritation caused by an underlying infection. In addition to these physical behaviors, pay attention to noticeable changes in your pet’s ears, especially in their condition. Look for redness, swelling, or unusual discharge, which may vary in color and consistency. A foul odor emanating from the ear can also signify an infection, further emphasizing the need for veterinary attention. Other symptoms include sensitivity to touch, excessive ear wax, and behavioral changes. If your dog becomes agitated, anxious, or withdrawn, this might indicate pain or discomfort related to the ear infection. It is essential to note any sudden shifts in your dog’s behavior or environment, as these can signal underlying health issues. Pet owners should monitor their dogs closely, especially in breeds predisposed to ear infections, such as floppy-eared varieties. Education about these symptoms empowers owners to act quickly, ensuring the best care for their loyal companions.
Veterinary professionals adopt a comprehensive approach when diagnosing ear infections in dogs. The history of the pet, including previous infections, allergies, and the duration of current symptoms, plays a crucial role in forming a diagnosis. A detailed physical examination is complemented by laboratory tests, which may include cytology, culture, or sensitivity tests. Cytology involves examining ear discharge microscopically to identify the presence of yeast, bacteria, or other pathogens. If a veterinarian suspects that allergies drive the recurrent infections, they may recommend allergy testing to pinpoint specific allergens. This step is essential because it forms the basis for future management options. Treatment plans often involve medications, such as antibiotics or antifungal agents, depending on the microorganisms involved. Addressing secondary issues, like allergies or skin conditions, may require additional therapies or lifestyle adjustments. Home care practices, like routine ear cleaning, can significantly reduce the recurrence of infections and promote long-term ear health. Owners should take an active role in managing their dog’s ear health, including regular check-ups to prevent future complications with ear infections.
Treatment Options and Recovery
Treatment for ear infections in dogs typically involves a combination of medications and ongoing care. Depending on the severity and cause of the infection, the veterinarian may prescribe topical or oral treatments. Topical medications are usually administered directly into the ear canal and may include antifungal agents, antibiotics, and anti-inflammatory drugs to control pain and swelling. The duration of the treatment will likely vary based on the infection’s severity and the dog’s response. It is essential for pet owners to administer all medications as directed, even if symptoms appear to resolve before completing the prescribed course. Incomplete treatment can lead to recurring infections and complications. Follow-up appointments with the veterinarian will ensure the infection is healing properly. In some cases, dogs may need re-evaluations to assess the effectiveness of the treatment regime and make any necessary adjustments. Home care practices, such as regular ear cleaning with veterinarian-approved solutions, can help facilitate the healing of the ear. Owner diligence and commitment to aftercare significantly influence the outcome and long-term well-being of the dog’s ear health.
Prevention is always better than cure, especially with ear infections in dogs. Regularly inspecting your dog’s ears and maintaining proper hygiene is essential to safeguarding against infections. Owners should learn how to clean their pet’s ears appropriately, using vet-recommended products specifically designed for canine ear care. Avoid using cotton swabs, which can push debris further into the ear canal. Instead, use moistened gauze or cotton balls to wipe the outer ear. Keeping ears dry is crucial, especially for breeds prone to moisture retention in their ear canals. After baths or swimming, always ensure to dry your dog’s ears thoroughly. Consider discussing preventative options with your veterinarian; some dogs may benefit from regular ear cleaning schedules, particularly breeds susceptible to frequent infections. Additionally, keeping your dog well-groomed will help reduce allergens that might contribute to ear issues. If your dog has underlying health problems, managing those proactively can also prevent future complications. Pet owners play an essential role in their dog’s health, and consistent ear care practices can significantly enhance their pet’s quality of life.
Seeking Professional Help
Knowing when to seek professional help is vital for your dog’s welfare. If you observe persistent signs of discomfort or infection symptoms like discharge, foul odor, or pain, a visit to the veterinarian is warranted. Often, pet owners may try home remedies or over-the-counter products, but these can sometimes do more harm than good if misapplied. Early intervention usually leads to less complex health challenges, reduces recovery time, and minimizes your dog’s suffering. Upon visiting a veterinarian, expect a thorough consultation regarding your dog’s health history, lifestyle, and behavior. This information allows for a well-rounded evaluation. The vet may recommend diagnostic procedures tailored to your pet’s condition. In some instances, surgical intervention might be necessary to correct underlying structural issues contributing to infections. Customized treatment plans that consider your dog’s specific needs can optimize recovery chance. Relying on a veterinary professional’s expertise is crucial in managing your dog’s ear health. Consistent follow-up appointments allow for ongoing monitoring, ensuring that future infections can be prevented efficiently.
In conclusion, understanding ear infections in dogs equips pet owners to recognize early symptoms and seek timely veterinary care. By familiarizing yourself with the signs of ear infections, you put your dog’s health first. Regular check-ups and discussions with your veterinarian can also significantly impact your dog’s ear health. Prevention measures, thorough ear examinations, and proper hygiene facilitate early detection of any potential issues. Adopting a proactive approach, including managing underlying health problems and understanding proper ear care, allows you to maintain your dog’s health effectively. Always stay vigilant for changes in your pet’s behavior, as these may indicate ear health issues that require immediate attention. Being an informed pet owner translates into better health outcomes and a comfortable life for your furry friend. Remember that partnership with your veterinarian is essential in safeguarding your dog’s ear health. Together, you can create a tailored wellness plan, ensuring a happy and healthy life for your beloved canine companion. With careful monitoring and appropriate care, your dog can enjoy a life free from the discomfort of ear infections.